Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMD) present a significant challenge in dental practice, requiring a deep understanding of diagnostic techniques and treatment options. For dentists practicing , staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in TMD management—including non-surgical, surgical, and neuromuscular dentistry (NMD) approaches—is essential to ensure optimal patient care.
What is TMD?
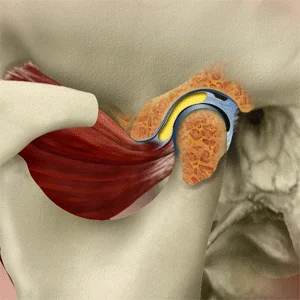
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is responsible for jaw movement and function. Dysfunction within this joint can lead to various symptoms, including pain, restricted mobility, joint sounds (such as clicking or popping), and associated issues like headaches or ear discomfort. TMD is multifactorial, with potential causes including:
- Occlusal disharmony
- Trauma or injury
- Bruxism (teeth grinding)
- Psychological stress leading to parafunctional habits
- Arthritis or degenerative joint disease
TMD Diagnosis: Clinical and Imaging Techniques
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to effective treatment. The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Patient History: Identifying pain patterns, triggers, parafunctional habits, and associated symptoms.
- Clinical Examination: Evaluating jaw movement, joint sounds, muscle tenderness, and occlusion.
- Imaging Techniques:
- Panoramic Radiographs: Useful for screening joint anatomy and pathology.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Preferred for assessing soft tissue structures like the articular disc.
- CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography): Provides detailed 3D visualization of bony structures.
Effective Treatment Options for TMD
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
Many cases of TMD can be effectively managed using conservative approaches, including:
-
Occlusal Splints and Orthotics: Custom-fitted splints help reposition the jaw and alleviate muscle tension. Common types include:
- Stabilization splints
- Repositioning splints
- Soft splints (for minor bruxism cases)
- Water splints (hydrostatic splints) to reduce joint strain
- Anterior deprogrammers for reducing clenching forces
-
Physical Therapy: Jaw exercises, posture correction, and myofascial release techniques can help relieve symptoms.
-
Pharmacologic Interventions: NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, and low-dose tricyclic antidepressants for chronic pain.
-
Botox Injections: Help relax overactive muscles and reduce symptoms in select patients.
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Stress management and habit modification for bruxism and other parafunctional habits.
2. Neuromuscular Dentistry (NMD)
NMD focuses on achieving optimal jaw alignment by analyzing and adjusting neuromuscular function. Common NMD approaches include:
- Electromyography (EMG): Assesses muscle function and detects imbalances.
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): Relaxes masticatory muscles to identify ideal occlusion.
- Computerized Jaw Tracking: Helps analyze mandibular movement and alignment for accurate treatment planning.
3. Surgical Interventions
Surgical treatments are considered when conservative methods fail or if there is significant structural damage. Surgical options include:
- Arthrocentesis: A minimally invasive procedure that flushes inflammatory mediators from the joint.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive technique for joint pathology diagnosis and treatment.
- Open Joint Surgery (Arthrotomy): Recommended for severe cases involving structural damage or dislocation.
- Total Joint Replacement (TJR): Considered for end-stage TMJ disorders with irreversible damage.
Tailoring Treatment to the Patient
Effective TMD management requires personalized treatment plans based on:
- The severity and nature of the patient’s symptoms
- Diagnostic findings and patient history
- Previous treatment outcomes
- The risk-benefit analysis of each treatment option
Conclusion
A multidisciplinary approach, incorporating general dentists, oral surgeons, physical therapists, and sometimes psychologists, is crucial for optimal TMD treatment outcomes. By staying informed about the latest treatment options, U.S. and U.K. dentists can provide evidence-based solutions for patients dealing with TMJ disorders.
For continuous professional development, attending TMJ-focused seminars, webinars, and training programs is essential to stay ahead in this evolving field.
Dr. Syed Nabeel, BDS, D.Orth, MFD RCS (Ireland), MFDS RCPS (Glasgow), is a dedicated dental professional with a special interest in Neuromuscular Dentistry (NMD). With over two decades of experience, he has been committed to diagnosing and managing occlusal and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders using a patient-centered approach that integrates the principles of neuromuscular occlusion.
Alongside his clinical work, Dr. Nabeel is deeply interested in digital dentistry and the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in dental practice. He believes that technology has the potential to enhance patient care by improving diagnostics and treatment precision. His work in this field reflects his curiosity and dedication to advancing dentistry in meaningful ways.
Dr. Nabeel also enjoys sharing knowledge and has been lecturing extensively on neuromuscular dentistry. His approach to teaching emphasizes practical insights, evidence-based methods, and a focus on patient well-being, making his sessions both engaging and valuable for fellow professionals. Additionally, he is a sought-after speaker and blogger on practice management, where he provides insights on optimizing workflow efficiency, patient engagement, and the integration of modern technology in dental practices.
Based in Mysore, India, Dr. Nabeel is the founder of Smile Maker, a practice where he strives to combine advanced diagnostic tools with personalized treatment plans to help patients with occlusal and TMJ-related concerns. With a strong commitment to continuous learning and improvement, Dr. Nabeel remains deeply invested in the evolving landscape of dentistry, always seeking ways to enhance patient outcomes with care and compassion.