The story of dental fillings dates back thousands of years, with ancient civilizations experimenting with ways to repair decayed teeth.
-
Ancient Times (2000 BC – 500 AD): The earliest known dental fillings date back to 6500 BC when beeswax was used to fill cavities in a Neolithic tooth discovered in Slovenia. In ancient Egypt, gold and other metals were used for dental restorations, and the Etruscans (around 700 BC) were early pioneers of using gold foil, demonstrating a deep understanding of biocompatibility.
-
Middle Ages (500 AD – 1500 AD): During this period, dental care was rudimentary. Materials like lead, tin, and crushed bone were used for fillings, but these often led to further complications due to their lack of ideal properties.
-
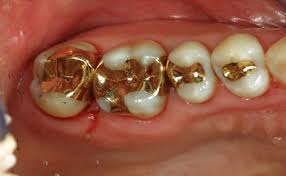
19th Century: The Birth of Modern Dentistry: The 1800s marked a significant shift in dental fillings with the introduction of amalgam, a mixture of mercury, silver, tin, and copper. Though initially controversial due to safety concerns, amalgam became the gold standard because of its durability and ease of use. Gold foil was also used for patients seeking more aesthetic and long-lasting restorations.
-
Early 20th Century: Silicate cements were introduced in the early 1900s as an aesthetic alternative to amalgam, though their lack of durability made them less popular. This period also saw the rise of porcelain inlays and crowns, paving the way for more advanced restorative techniques.
The Present: A Blend of Science and Artistry
Today, dental fillings represent the culmination of advancements in materials science, adhesive dentistry, and digital technology. Modern fillings not only emphasize function but also biocompatibility and aesthetics.
-
Composite Resins: Composite fillings have revolutionized restorative dentistry, offering excellent aesthetics and bonding directly to the tooth structure. With advancements in nanotechnology, modern composites are stronger, more wear-resistant, and capable of mimicking the natural translucency of enamel.
-
Glass Ionomer Cements (GIC): GICs are commonly used in pediatric dentistry and non-load-bearing restorations. They release fluoride, promoting preventive benefits, and bond well with both enamel and dentin.
-
Ceramics and CAD/CAM Technology: The integration of CAD/CAM systems has transformed dental restorations. Materials like lithium disilicate and zirconia offer exceptional strength and aesthetics, enabling same-day crowns, inlays, and onlays.
-
Minimally Invasive Dentistry: Modern dentistry focuses on preserving as much natural tooth structure as possible. Techniques such as air abrasion, laser dentistry, and bioactive materials help achieve this goal.
-
Amalgam’s Decline: Despite its long history, amalgam’s use has declined due to concerns over mercury toxicity and the increasing demand for more aesthetically pleasing and biocompatible options.
The Future: What’s Next for Dental Fillings?
The future of dental fillings is incredibly promising, as technological advances continue to shape the field of restorative dentistry. Here’s a glimpse into what lies ahead:
-
Bioactive and Biomimetic Materials: Future fillings will do more than just fill cavities. Bioactive materials containing calcium phosphate or bioactive glass will actively promote remineralization, while biomimetic restorations will replicate the natural properties of enamel and dentin for long-term durability and function.
-
3D Printing and Digital Dentistry: 3D printing is set to revolutionize dental restorations. Imagine printing custom composite or ceramic fillings chairside within minutes! Digital workflows will continue to streamline processes, reducing turnaround times and enhancing precision.
-
Regenerative Dentistry: Stem cell research and tissue engineering offer the potential to regenerate damaged tooth structures. While still in its early stages, this field could eventually make traditional fillings obsolete by enabling the regrowth of enamel and dentin.
-
Smart Fillings: The future might include fillings embedded with sensors that monitor oral health in real time, detecting early signs of decay or infection. This would allow dentists and patients to take proactive measures for maintaining oral health.
-
Eco-Friendly Materials: As sustainability becomes a global priority, the dental industry will likely shift toward eco-friendly materials and processes. Biodegradable composites and mercury-free alternatives will become the new standard.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Innovation
The journey from beeswax to biomimetics in dental fillings reflects the ingenuity and dedication of dentists, researchers, and innovators throughout history. As we look to the future, one thing is clear: restorative dentistry will continue to push boundaries, blending science, technology, and artistry to improve patient care.
As dentists, we are not just filling cavities – we are restoring smiles, confidence, and quality of life. And that’s something to be proud of. The next time you place a filling, take a moment to appreciate how far we’ve come and get excited about where we’re headed. The future of dentistry is bright, and it’s in our hands to shape it.
Keep innovating, keep learning, and keep smiling!
Written by Dr. Hajeera Banu
Dr. Hajeera Banu is a skilled dentist specializing in restorative dentistry, implants, and aligners. With a degree from RGUHS (2014), Dr. Banu has built a respected private practice in Mysore, India. Passionate about providing the best care to her patients, she also enjoys blogging, cooking, and traveling. With a commitment to staying current with the latest developments in dentistry, she continues to explore innovative solutions for improving patient outcomes.